Agriculture has always faced challenges. Today, in addition to extreme weather events, there are also fertiliser regulations and the elimination of active substances and products in plant protection products. The challenges are increasing and, in addition to the use of top rapeseed varieties, the agronomic/plant cultivation approach plays an important role. Companion crops are an instrument to counteract current challenges, such as reduced fertilisation and discontinuation of active substances/plant protection products. Depending on the site conditions, weather and sowing technique, a companion crop can become well established and show its advantages.
Advantages of rapeseed companion crops
These advantages are based, among other things, on the fact that companion crops strengthens the soil, especially if they consist of different, coordinated plant species. Here, the stabilisation of the soil structure is to be mentioned, which comes along with a combination of different root systems. This combination of different plant species can also improve the nutrient dynamics. Through the different root systems, different areas in the soil are opened up and nutrients that may not be within reach for the rapeseed are utilised. Furthermore, root exudates can increase the nutrient availability of certain nutrients. Root exudates differ depending on the plant species, so here again; the combination of different plant species is advantageous. When the companion crops die over the winter, nutrients are released through decomposition and mineralisation, which can be made available to the rapeseed or the following crop later. As soon as companion crops contain legumes, additional nitrogen can be fixed. However, care should be taken that the legumes are not sown too late so that they can develop sufficiently before winter.
Well-established companion crops increase the soil cover. Faster soil cover can reduce evaporation of soil water and reduce erosion. Furthermore, a well-established companion crop can suppress weeds if the weed pressure on the field is not too high.
Trials have shown that insect pests can be distracted by rapeseed. A well-developed companion crop can, for example, irritate the flea beetle. This can support insecticide management. However, the extent to which an insecticide measure is additionally necessary should still be closely monitored by observing damage thresholds.
It is clear that, in addition to the main crop, rapeseed, soil nutrition and fertility are also supported by companion crops. This is an aspect that is very important, especially in the long term, to enable yield stability of all crops in the crop rotation.

On the right rapeseed without companion crops, on the left and in the middle with two different companion crops.
Seeding and herbicide management
There are various options available for sowing, which depend, among other things, on the machinery available on the farm. If a two-tank sowing machine is available, this can be used very well. Otherwise, if the thousand seed weight distribution of the companion crop is not too different from the thousand seed weight of the rapeseed, a single-tank sowing machine can be used. Or the companion crop is sown first and the rapeseed is sown in a second pass. In addition, rapeseed can also be sown into an existing stand of companion crop. In this case, the companion crop is drilled earlier to ensure sufficient development of the legumes before winter, before the rapeseed is drilled later.
The use of herbicides is also possible in companion crops. To minimise damage to the companion crop, a closer look should be taken at the herbicide used. The table shows the phytotoxicology of individual plant protection products/active substances on exemplary companion crop components.
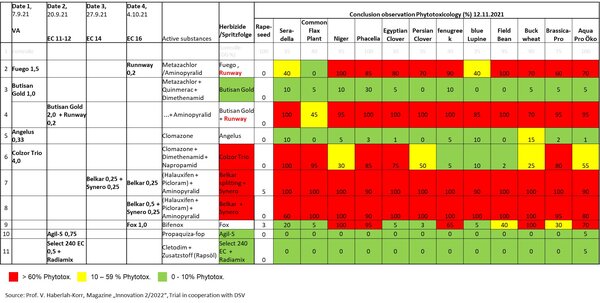
The table also shows, however, that there are sufficient options if the companion crop is to be removed, for example after a mild winter.
TerraLife® Brassica Pro - the rapeseed companion crop mixture
Through many years of experience in the division of cover crops and companion crops, with TerraLife® Brassica Pro we have succeeded in putting together a companion crop mixture for rapeseed that can fully exploit its advantages. Synergies can be optimally utilised through the intelligent combination of different components. This way the rapeseed can be supported. The carefully selected combination of different plant species promotes the soil structure. Through interaction of the different plant species with the soil, the nutrient dynamics can be balanced throughout the entire growth phase. The varied plant community ensures that the soil life is fed in a more diverse way without competing with the main crop rapeseed. The C/N ratio is positively influenced by the high proportion of legumes. In addition, the varieties within the TerraLife® Brassica Pro are freezing down very good.